By Ben Fuchs | PharmacistBen

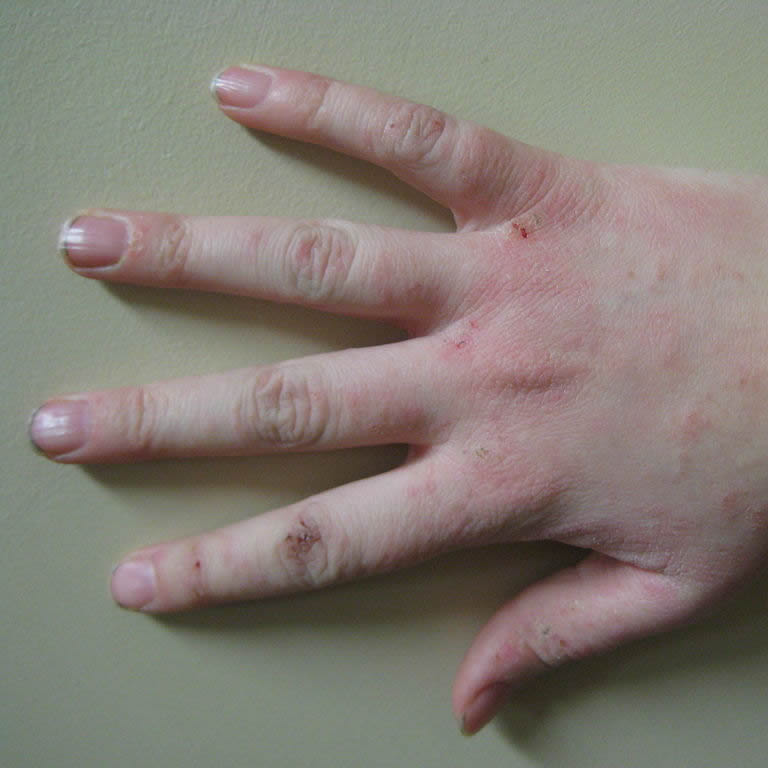
Eczema or Dermatitis of the hand. Image credit: James Heilman, MD (Own work) [CC BY-SA 3.0 or GFDL ], via Wikimedia
“Skin cells” make vitamin D, they produce prodigious quantities of skin fats (lipids), and they are also the source of many hormone chemicals. Some, like cortisol, are involved in obvious skin functions like protection. Others, like the nervous system’s serotonin and dopamine, make the skin a type of brain appendage. Not to forget pheromones, which are involved in less obvious skin functions, like signaling, sexual attraction and fertility.
One of the less apparent roles of keratinocytes (“skin cells”) involves the production of inflammatory chemicals known as prostaglandins and cytokines. Although these chemicals are supposed help keep local invaders sequestered, they also can be produced and activated in a less specific way by systemic immune responses to foods or other ingested substances. When this occurs, regulation and control of skin cell production and development can be impaired. They can cause cells to grow in a messed up, chaotic, out-of-control fashion. This is at least partially the genesis of many skin health issues, including acne and psoriasis.
One of the more troubling inflammatory skin health issues is eczema, an itchy, unpleasant condition that affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Here in the USA, a substantial proportion of the population suffers from the uncomfortable and sometimes unattractive symptoms of eczema. According to the American Eczema Association, one out of ten (nearly 32 million people) have the disease, which is characterized by defects in the development of the skin surface barrier. It’s most notably caused by the inflammation associated with the secretion of defensive prostaglandins and cytokines, stimulated by perceived threats, whether introduced to the skin internally from the food toxicity and digestive difficulties via the blood or occasionally by topical contact.
Although eczema has been a recognized skin disease for millennia, (ancient Egyptian recommendations recorded on papyrus suggest honey salves as a treatment), the medical model remains so mystified by how to address it, that most modern treatments available today (typically steroid creams) haven’t substantially changed in decades.
The inflammatory aspect of eczema makes it a classic type defensive skin disease. Inflammation is the calling card of the immune system, and eczematous skin is a sign that the body is protecting itself. This protective response is what we call inflammation, and it affects how skin cells grow and ultimately how surface barrier is formed. The end result is the raw, rashy symptomology of eczema.
While the dermatologist strategy for dealing with this distress and discomfort involves suppression of the defenses with steroid creams and ointments, at best this can only give temporary and symptomatic relief. The most effective, intelligent and non-medical way to address eczema is to eliminate the stimulus of the defensive response by first asking the logical question: what is the offending agent? Food and digestion are almost always involved, and yes, gluten is a possible suspect. But there’s no way of knowing what you are reacting to without linking skin flare-ups and digestive symptoms (like gas, constipation or heartburn) to specific foods.
Nutritional supplements can be helpful too. Essential fatty acids, fatty vitamins, especially A, (20, 000 iu daily), D (5000 iu daily), lots of sunshine exposure are important. While minerals like zinc picolinate (50mg daily) and selenium Monomethionine or chelate (400 mcg daily) can be helpful too. I hope that helps. Also, it’s important to keep in mind: It’s not just what you “take”, it’s also what you absorb. Digestive distress and malabsorbtion (especially fat mal-absorption) often accompany eczema as well as other skin conditions.